Income Tax Slab for Senior & Super Senior Citizens
As per the Income Tax Act, resident individuals aged 60 years and above but below 80 years during the financial year are classified as senior citizens, while resident individuals aged 80 years or above are classified as super senior citizens. These categories of individuals enjoy higher exemption limits under the Old Tax Regime. However, there is no such provision in the New Tax Regime.
In Old Tax Regime, senior citizens enjoy an exemption limit of up to Rs. 3 lakhs and super senior citizens enjoy an exemption limit of up to Rs.5 lakhs.
Age Eligibility Rules for Senior and Super Senior Citizens under Income Tax

For income tax purposes, an individual is considered to have attained a specific age on the day immediately preceding their birthday. This rule is used to determine eligibility for tax benefits available to senior and super senior citizens. The age rules for senior citizens and super senior citizens are as follows:
- A resident individual qualifies as a senior citizen if they attain the age of 60 years at any time during the financial year.
For example, if a person’s 60th birthday falls on 1 April 2026, they are deemed to have completed 60 years on 31 March 2026.
- Accordingly, they become eligible for the higher basic exemption limit of Rs.3 lakh under the old tax regime for that financial year.
- The same age-attainment principle applies for determining eligibility as a super senior citizen (80 years and above).
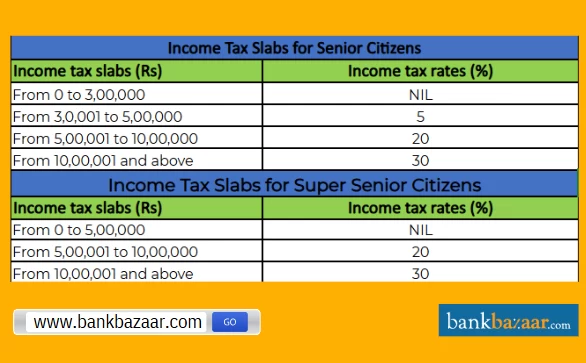
Income Tax Slab for Senior Citizens as per Old Tax Regime
The income tax slab for senior citizens as per old tax regime is as follows:
Income Range | Income Tax Rates |
Up to Rs. 3 lakhs | Nil |
Rs. 3 lakhs to Rs. 5 lakhs | 5% |
Rs. 5 lakhs to Rs. 10 lakhs | 20% |
Above Rs. 10 lakhs | 30% |
Income Tax Slab for Super Senior Citizens as per Old Tax Regime
The income tax slab for super senior citizens as per old tax regime is as follows:
Income Range | Income Tax Rates |
Up to Rs. 5 lakhs | Nil |
Rs. 5 lakhs to Rs. 10 lakhs | 20% |
Above Rs. 10 lakhs | 30% |
Income Tax Slab for Senior Citizens as per New Tax Regime
Senior and super senior citizens do not enjoy any special benefits under the New Tax Regime. Under the New Tax Regime, a uniform tax slab structure applies to all taxpayers, including senior and super senior citizens. However, opting for this regime requires taxpayers to give up several deductions and exemptions available under the old regime. The income tax slabs for senior citizens as per new tax regime is as follows:
Income Range | Income Tax Rates |
Up to Rs. 4 lakhs | Nil |
Rs. 4 lakhs to Rs.8 lakhs | 5% |
Rs. 8 lakhs to Rs.12 lakhs | 10% |
Rs.12 lakhs to Rs.16 lakhs | 15% |
Rs.16 lakhs to Rs. 20 lakhs | 20% |
Rs. 20 lakhs to Rs. 24 lakhs | 25% |
Above Rs. 24 lakhs | 30% |
Cess and Surcharge for Senior and Super Senior Citizens
The tax for calculated senior and super senior citizens is increased by a ‘Health and Education Cess’ of 4% for both old and new tax regimes. However, a surcharge is levied depending on the taxpayer’s total income:
Income Range | Surcharge Rate |
Above Rs.50 lakhs | 10% |
Above Rs.1 crore | 15% |
Above Rs.2 crore | 25% |
Above Rs.5 crore | 37% |
Note :Do note that a maximum of 25% surcharge is applicable under the New Tax Regime.
Income Tax Calculation for Senior Citizens FY 2025-26
The income tax for senior citizens is calculated based on the basic salary, house rent allowance, fixed allowances, and other sources of income. However, the senior citizen receives higher exemption limit compared to individuals who are below 60 years old.
In order to calculate the income tax for a senior citizen, all the income is taken into consideration along with the allowable deductions and the income tax slab for FY 2024-25. Once you have all the details, the tax calculator can be used to determine your taxable income.
Under this new tax regime, there is no higher tax exemption limit for senior citizens (between the age of 60 and 80) or for super senior citizens (above the age of 80). Given below are the various tables for the Income Tax Slabs for the FY 2024-25 under the new tax regime
Income Tax Benefits for Senior and Super Senior Citizen
The income tax benefits that can be availed by senior and super senior citizens are as follows:
- Interest Income
- Senior citizens (Indian residents) do not have to pay tax in case they are earning an interest of up to Rs.50,000 in a financial year. The benefit is provided under Section 80TTA. Form 15H must be submitted when the ITR is filed.
- Do note that Rs.50,000 deduction is the total deduction available, it is not per account. The deduction under Section 80TTA is applicable only under Old Tax Regime.
- Advance Tax
- Senior citizens do not have to pay advance tax during the year as they do not have business income. They only have to pay the Self-Assessment (SA) Tax which is done after calculation of the final tax liability for the financial year.
- Reverse mortgage
- As per the reverse mortgage scheme, senior citizens can mortgage their house to a bank or lender.
- In return, the bank provides the loan amount in Equated Monthly Instalments (EMIs). The loan is settled when the borrower passes away or chooses to repay it.
- At that stage, the bank sells the house on the borrower’s behalf. The sale proceeds are used to repay the outstanding loan amount.
- Any excess amount from the sale is paid to the borrower or their legal heirs. Do note that capital gains tax is not payable by the senior citizen on such a transfer.
- Specified Disease Treatment:
- Senior citizens can claim a deduction of up to Rs.1 lakh under Section 80DDB in case of any medical expenses incurred for specified diseases.
Deduction Available for Senior and Super Senior Citizens
In case senior citizens want to calculate the amount of tax that must be paid, the income that is generated from all sources must be added. As per the slabs under the old income tax slabs the below-mentioned exemptions and deductions are allowed:
Sections | Deductions |
Section 80C | Up to Rs.1.5 lakh can be claimed under the below-mentioned investments: National Savings Certificate, Senior Citizen Savings Scheme, Life Insurance Premium, Public Provident Fund, Equity Linked Savings Scheme, 5-year Fixed Deposit. |
Section 80CCC | Rs.50,000 can be claimed under Section 80CCD(1B) and an additional deduction can be claimed under Section 80CCD(2) |
Section 80D | Up to Rs.50,000 can be claimed. |
Section 80DD | Depending on the disability, up to Rs.1.25 lakh can be claimed. |
Section 80DDB | Up to Rs.1 lakh can be claimed. |
Section 80G | Based on the charity, the amount that can claimed will vary. |
Section 80GGC | Any contributions made towards an electoral trust or political party. |
Section 80RRB | Up to Rs.3 lakh can be claimed. |
Section 80TTB | Up to Rs.50,000 can be claimed. |
Section 80U | Depending on the severity of the disability, up to Rs.1.25 lakh can be claimed. |
Senior Citizens Tax Exemptions
A senior citizen is an individual resident who is 60 years old or more but below 80 years as on the last day of the previous year. Senior citizens at source of income include pension, rental income, interest on savings, fixed deposits, senior citizen saving scheme, reverse mortgage, and post office scheme.
- Health Insurance: Deductions of up to Rs.50,000 per annum can be claimed by senior citizens towards their health insurance premium and/or medical expenses under Section 80D. In the case of dependent seniors, a deduction of up to Rs.1 lakh can be claimed for critical illnesses that have been specified previously. This falls under Section 80DDB.
- Pension: For pensions there is a standard deduction of Rs.50,000 per year. This is for pensions in the form of annuity payments which are taxable just like the salaried income. It falls under Section 80D.
- Interest Income from Deposits: Maximum of up to Rs.50,000 per annum is Deducted under Section 80TTB.
According to a Central Board of Direct Taxes directive, cases of senior citizens cannot be scrutinised unless an assessment is necessary on the basis of credible information.
Income Tax Filing for Senior Citizens
The senior citizens are required to file the income tax return to claim their tax refund. The following Income Tax Return (ITR) forms are required to be filled by the senior citizens:
ITR I - Individual whose total Income Includes:
- Salary or pension
- Income from house or property (excluding incidents where loss is brought forward from previous financial years)
- Income from the other sources (excluding income from horse racing or winning lottery)
ITR 2 - Individual whose total Income Includes:
- Salary or pension
- Income from house or property
- Capital gains
- Income from the other sources (includes winning from horse racing and lottery)
- Incidents where the income of another individual, such as spouse or other member has to be combined with the income of the individual
Union Budget 2025: Threshold of TDS
Under the Union Budget 2025, the Finance Minister announced a proposal on the rationalization of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS). The threshold of tax deduction on interest income from deposits for senior citizens has doubled from Rs.50,000 to Rs.1 lakh.
FAQs on Income Tax for Senior Citizens
- How much is the income tax exemption limit for senior citizens?
The income-tax exemption limit is Rs.3 lakh for senior citizens and Rs.5 lakh for super senior citizens as per the old tax regime, while the new tax regime offers no separate higher exemption based on age.
- What is the oldest age at which seniors must file an income tax return?
This is based on the elder citizen's basic income rather than their age (this includes rent allowances, fixed and other sources of income). The exemption limit for senior citizens is Rs. 3 lakhs and for super senior citizens is Rs.5 lakhs.
- What is the usual senior tax deduction?
The standard deduction for seniors is Rs.50,000, as per the most current revisions to the Income Tax Act.
- What is the maximum tax advantage for senior citizen health insurance?
Senior citizens get a deduction of up to Rs.50,000 for health insurance premiums paid for self-and/or spouse. Do note that this also includes preventive health check-up expenses of up to RS.5,000 within this overall limit, and not over and above it.
- What does marginal relief mean?
Marginal relief is a tax benefit offered by the government that ensures a taxpayer does not end up paying more tax just because their income slightly exceeds a threshold where surcharge becomes applicable.
News about Income Tax Slab for Senior Citizens
Union Budget 2026: No Change in Income Tax Slabs for Senior Citizens
In the Union Budget 2026, the Finance Minister did not announce any changes in tax slabs or basic exemption limits. The slabs that were announced in the previous budget remain in force for FY 2026-27 (AY 2027-28).

Disclaimer
Credit Card:
Credit Score:
Personal Loan:
Home Loan:
Fixed Deposit:
Copyright © 2026 BankBazaar.com.